Diagnosis Visit for Joint Hypermobility / Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
The evaluation for hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (hEDS) is grounded in the 2017 diagnostic criteria established by the International EDS Consortium. Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes (EDS) encompass a heterogeneous group of heritable connective tissue disorders, primarily characterized by joint hypermobility, skin hyperextensibility, and tissue fragility. This comprehensive diagnostic framework for hEDS includes not only an assessment of these hallmark features but also a thorough evaluation of related neuromuscular conditions, other connective tissue disorders with known genetic origins, and potential autoimmune conditions, which may present with overlapping symptoms.
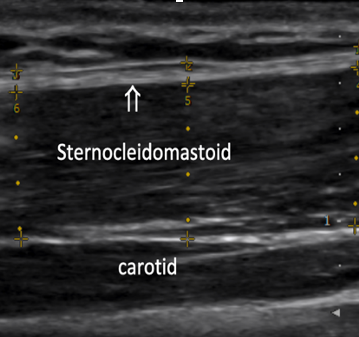
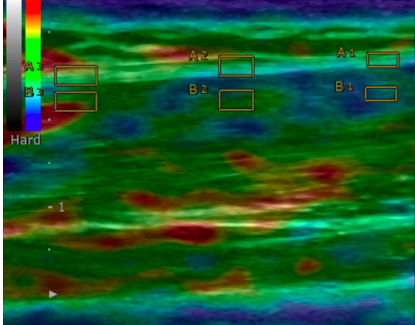
A key component of this evaluation is the use of ultrasound elastography, a specialized imaging technique that measures both the thickness and stiffness of deep fascia. In hypermobile spectrum disorders, excess extracellular matrix deposition leads to an increase in deep fascia thickness, while the stiffness of the fascia, as assessed by elastography, is often lower than normal. This reduction in stiffness reflects underlying connective tissue changes that contribute to the clinical manifestations of hEDS. The integration of these advanced diagnostic tools aids in a more accurate diagnosis and provides insights into the structural abnormalities of the fascia and tendons, facilitating targeted therapeutic strategies.
-
Wang TJ, Stecco A. Fascial thickness and stiffness in hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2021 Dec;187(4):446-452. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31948. Epub 2021 Nov 6. PMID: 34741592. https://sedinfrance.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Wang2021-Fascial-thickness-and-stiffness-in-hypermobile-Ehlers%E2%80%90Danlos-syndrome.pdf
-
Malfait F, Francomano C, Byers P, Belmont J, Berglund B, Black J, Bloom L, Bowen JM, Brady AF, Burrows NP, Castori M, Cohen H, Colombi M, Demirdas S, De Backer J, De Paepe A, Fournel-Gigleux S, Frank M, Ghali N, Giunta C, Grahame R, Hakim A, Jeunemaitre X, Johnson D, Juul-Kristensen B, Kapferer-Seebacher I, Kazkaz H, Kosho T, Lavallee ME, Levy H, Mendoza-Londono R, Pepin M, Pope FM, Reinstein E, Robert L, Rohrbach M, Sanders L, Sobey GJ, Van Damme T, Vandersteen A, van Mourik C, Voermans N, Wheeldon N, Zschocke J, Tinkle B. The 2017 international classification of the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2017 Mar;175(1):8-26. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31552. PMID: 28306229.
SCM Fascia Thickness (normal < 1.5mm) SCM Strain index (normal SI approximately 2.1)
Diagnosis Visit for Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, and Associated Conditions
This visit is designed to evaluate and address hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (hEDS) and its associated comorbidities, including upper cervical instability, mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), dysautonomia, fascia dysfunction, and neurodiversity. During the visit, we will conduct a comprehensive assessment to identify the presence of hypermobility and related issues, particularly in the cervical spine, which is prone to instability in hEDS patients. We will also evaluate the role of dysautonomia and POTS, both of which can significantly impact quality of life, often causing fatigue, dizziness, and difficulty with daily activities. MCAS, a common comorbidity, will be addressed through a personalized treatment plan to manage allergic-like symptoms triggered by mast cell dysfunction. Fascia dysfunction, frequently present in EDS, will be treated using fascial sequencing manual therapy to reduce densification and improve tissue mobility. Neurodiversity considerations, such as sensory processing differences, may be evaluated.
Injection Visit
Injection visits involve a tailored combination of techniques based on the specific pathology identified through ultrasound imaging. These techniques may include fascial layer-specific hydromanipulation, prolotherapy, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy.
- Fascial Layer-Specific Hydromanipulation: This technique focuses on applying fluid dynamics to target specific layers of fascia, promoting tissue mobility while reducing restrictions and densification that may contribute to pain and dysfunction. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33419263/
- Prolotherapy: This regenerative injection therapy involves injecting a dextrose solution into damaged tissues to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes. It aims to enhance the stability and function of the affected area by promoting collagen production and tissue repair. Tetradecyl per Fraser Burling's landmark paper is an option: https://bmjopensem.bmj.com/content/5/1/e000481
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP involves extracting a small amount of the patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting this solution into the area of concern. The growth factors in PRP can accelerate healing and reduce inflammation in damaged tissues.
- Hydrodissection of Nerves: A minimally invasive procedure used to release nerves entrapped within fascial planes. By injecting fluid (typically saline or a combination of anesthetic agents), hydrodissection helps free the nerve from surrounding tissues and relieve pain. This technique is enhanced by ultrasound guidance to ensure precision and effectiveness.
- Botox/Xeomin Injections with Fascial Sequencing Technique: Utilized to relax hyperactive muscles and manage myofascial pain. This method incorporates ultrasound-guided fascial sequencing to target specific areas, improving muscle balance and reducing muscle spasms that may contribute to joint instability in patients with hEDS.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34754601/
By utilizing these techniques in combination, injection visits aim to provide a comprehensive approach to addressing fascial and musculoskeletal issues, ultimately improving patient outcomes and enhancing overall function. Each treatment plan is customized based on individual needs and the specific findings observed during ultrasound evaluation, ensuring targeted and effective care.
Fascia Visit: diagnostic and therapeutic fascial sequencing manual therapy
This visit involves a comprehensive diagnostic and therapeutic approach using fascial sequencing manual therapy. It begins with a systematic assessment to identify and treat fascial densifications that may be contributing to movement restrictions or pain. Following this, specific stabilization exercises are introduced to target underlying neuromuscular control dysfunction. These exercises are designed to enhance musculoskeletal stability, improve movement patterns, and reduce the risk of further injury. The combined approach addresses both the fascial system and neuromuscular coordination to optimize long-term functional outcomes.
Integrative Intervention Plan Visit
This visit provides a comprehensive, in-depth assessment of your personalized treatment plan from a holistic perspective. It includes detailed recommendations tailored to your specific needs, covering manual therapy for fascial and musculoskeletal health, movement therapy to enhance flexibility and joint stability, and medications for symptom management. Nutritional advice will be provided to support tissue repair and reduce inflammation, while alternative interventions, such as supplements or integrative therapies, are explored to promote overall well-being. Neurodiversity considerations, such as sensory processing differences, will be integrated into the treatment plan to ensure a holistic and patient-centered approach to care. This approach ensures all aspects of your health are addressed for optimal management.
Dr. Wang's lecture of the topic:







